ChatGPT Drives 71% of Enterprise Data Breaches, Study Finds
A new study reveals that ChatGPT is responsible for 71% of corporate data breaches, exposing critical vulnerabilities in how enterprises deploy generative AI tools without proper security safeguards.
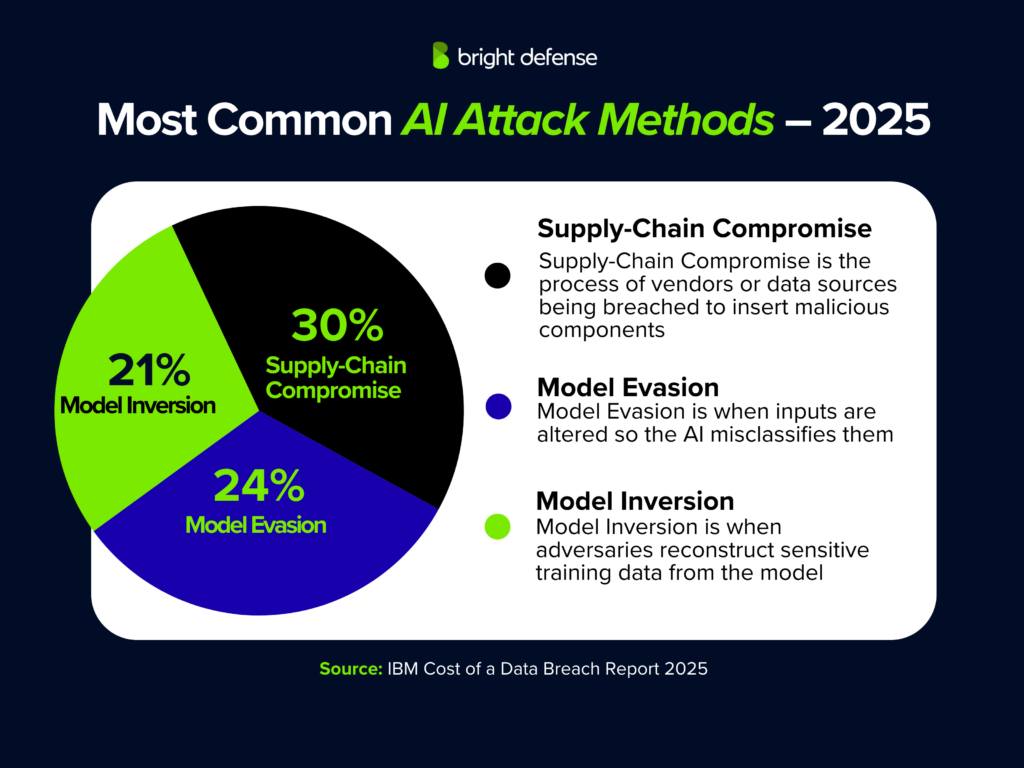
The AI Security Crisis Deepens
The enterprise rush to adopt generative AI has collided with reality: according to recent research, ChatGPT is now responsible for 71% of corporate data breaches tied to generative AI tools. This staggering figure underscores a fundamental disconnect between the speed of AI adoption and the maturity of security practices in corporate environments.
The statistic reveals not a flaw in ChatGPT itself, but rather a systemic failure in how organizations deploy and govern access to powerful AI systems. Employees, often without explicit security training, are pasting sensitive information—customer records, financial data, proprietary code, and trade secrets—directly into public AI interfaces, creating an unprecedented attack surface.
Why ChatGPT Became the Breach Vector
The dominance of ChatGPT in breach statistics stems from several converging factors:
- Ubiquity: ChatGPT's free tier and ease of access make it the default choice for employees seeking quick productivity gains
- Lack of governance: Most organizations lack policies restricting what data employees can input into public AI services
- Data retention concerns: According to security experts, user inputs to ChatGPT may be retained and used to train future models, creating long-term exposure risks
- Insider threat amplification: Research shows that insider threats account for a significant portion of data breaches, and AI tools have become an unwitting vector for this risk
The problem isn't malicious intent—it's negligence at scale. An employee asking ChatGPT to "summarize this customer database schema" or "debug this authentication code" may inadvertently expose critical infrastructure details to a system with no enterprise security controls.
The Broader AI Security Landscape
This ChatGPT finding sits within a larger ecosystem of AI-related security risks. Industry analysis identifies multiple attack vectors beyond data leakage, including prompt injection attacks, model poisoning, and AI-generated phishing content. The 71% figure specifically captures data exfiltration incidents, but the full threat surface is considerably broader.
Organizations are also grappling with data privacy implications, particularly around GDPR and other regulatory frameworks. Feeding personal data into third-party AI services creates compliance liabilities that many enterprises have yet to fully assess.
What Organizations Must Do Now
The path forward requires a multi-layered approach:
Immediate actions:
- Implement clear policies on what data can be input into public AI services
- Deploy data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and block sensitive information flows to external AI platforms
- Conduct security awareness training focused on generative AI risks
Medium-term strategies:
- Evaluate enterprise-grade AI solutions with built-in security controls and data retention guarantees
- Establish AI governance frameworks that classify data sensitivity and map it to approved tools
- Monitor emerging cybersecurity statistics to stay informed on evolving threats
Long-term considerations:
- Develop internal AI capabilities that keep sensitive data within corporate infrastructure
- Participate in industry standards development for responsible AI deployment
- Budget for incident response capabilities specifically designed for AI-related breaches
The Accuracy Problem Compounds the Risk
Adding another layer of concern, research on AI hallucinations reveals that ChatGPT generates plausible-sounding but false information at measurable rates. This means employees may not only be leaking real data but also receiving unreliable outputs that they then act upon—potentially compounding security mistakes.
The Bottom Line
The 71% figure is a wake-up call, not a condemnation of AI itself. Generative AI tools offer genuine business value, but deploying them without security governance is equivalent to leaving sensitive files on a public server. According to risk assessments, AI-related risks are now among the top concerns for enterprise risk managers.
The enterprises that will thrive in the AI era are those that treat security and governance as prerequisites for adoption, not afterthoughts. The 71% statistic represents a massive opportunity for organizations to get ahead of the curve—before their competitors learn the hard way.



